Swift Date Time Formatting
Consider formatters. Both Swift and Cocoa/Cocoa touch support a number of these, ranging from numbers and currency to dates and times. They are a natural interpolation fit. For example, dates are easy right out of the box. Just pass a formatter and you’re done. Note that I skip the formatter label. You’ll see why in just a second. The JSON date format for a Date got the value of 57786402. This almost looks like a unix epoch timestamp, but if you put it into an online converter it’ll come out as @ 4:06pm. It’s not a unix timestamp. It’s actually using a different reference date – 2001 instead of 1970. Standard Approach, using a DateFormatter 🗓 As mentioned, the DateFormatter approach set's up the timezone, set's up the string format for the date, and then uses the formatter to provide the string from Foundation's date object! Looking at this a bit more in-depth, notice that the timeZone on the formatter is set to the.current timeZone. The Date struct is used to represent dates and times in Swift 5, and it’s designed to do so in the most flexible way possible: as a number of seconds relative to the start of the Third Millennium, January 1, 2001, 00:00:00 UTC.

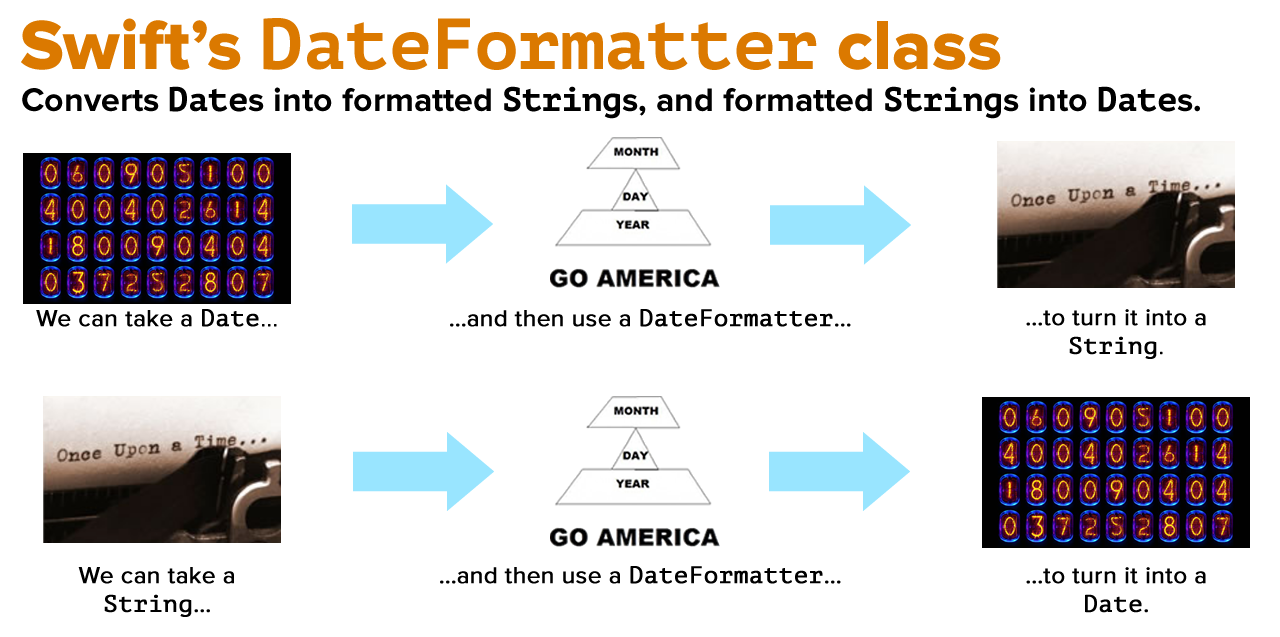
Overview
Swift Date Format

Swift is a programming language for macOS, iOS, watchOS and tvOS. Chances are if you are developing a mobile app for iphones, ipads or iwatches, you’ll need to learn swift. Date Time Formatting in Swift is based off of the DateFormatter class which can be used to manipulate dates and times. An Instance of DateFormatter creates a string representation of NSDate objects, and can also convert textual representations of dates and times into NSDate objects.
Patterns
| Characters | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Year | ||
y | 2018 | Year, no padding |
yy | 18 | Year, two digits (padding with a zero if necessary) |
yyyy | 2018 | Year, minimum of four digits (padding with zeros if necessary) |
| Quarter | ||
Q | 2 | The quarter of the year. Use QQ if you want zero padding. |
QQQ | Q2 | Quarter including “Q” |
QQQQ | 2nd quarter | Quarter spelled out |
| Month | ||
M | 11 | The numeric month of the year. A single M will use ‘1’ for January. |
MM | 11 | The numeric month of the year. A double M will use ’01’ for January. |
MMM | Nov | The shorthand name of the month |
MMMM | November | Full name of the month |
MMMMM | N | Narrow name of the month |
| Day | ||
d | 26 | The day of the month. A single d will use 1 for January 1st. |
dd | 26 | The day of the month. A double d will use 01 for January 1st. |
F | 4th Wednesday in December | The day of week in the month |
E | Weds | The day of week in the month |
EEEE | Wednesday | The full name of the day |
EEEEE | W | The narrow day of week |
| Hour | ||
h | 5 | The 12-hour hour. |
hh | 05 | The 12-hour hour padding with a zero if there is only 1 digit |
H | 17 | The 24-hour hour. |
HH | 17 | The 24-hour hour padding with a zero if there is only 1 digit. |
a | PM | AM / PM for 12-hour time formats |
| Minute | ||
m | 25 | The minute, with no padding for zeroes. |
mm | 25 | The minute with zero padding. |
| Second | ||
s | 1 | The seconds, with no padding for zeroes. |
ss | 01 | The seconds with zero padding. |
| Time Zone | ||
zzz | EST | The 3 letter name of the time zone. Falls back to GMT-08:00 (hour offset) if the name is not known. |
zzzz | Eastern Standard Time | The expanded time zone name, falls back to GMT-08:00 (hour offset) if name is not known. |
zzzz | CST-04:00 | Time zone with abbreviation and offset |
Z | -0400 | RFC 822 GMT format. Can also match a literal Z for Zulu (UTC) time. |
ZZZZZ | -04:00 | ISO 8601 time zone format |